AI-FACTORY
Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0
Links:
- Broadcast during the Navarra Televisión SINAI Space
- Report on Navarra Capital "Las empresas se interesan por el gemelo digital que permite ahorrar en calefacción"
Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0
Links:
Ai-FACTORY is a project focused on energy savings in industrial climate control systems by using high-level artificial intelligence. In this project, VW NA, which consumes a large amount of natural gas for that purpose, was the company that supported the project. In addition to being a process found throughout industry, this problem, especially in the automotive sector, is the primary energy consumption.
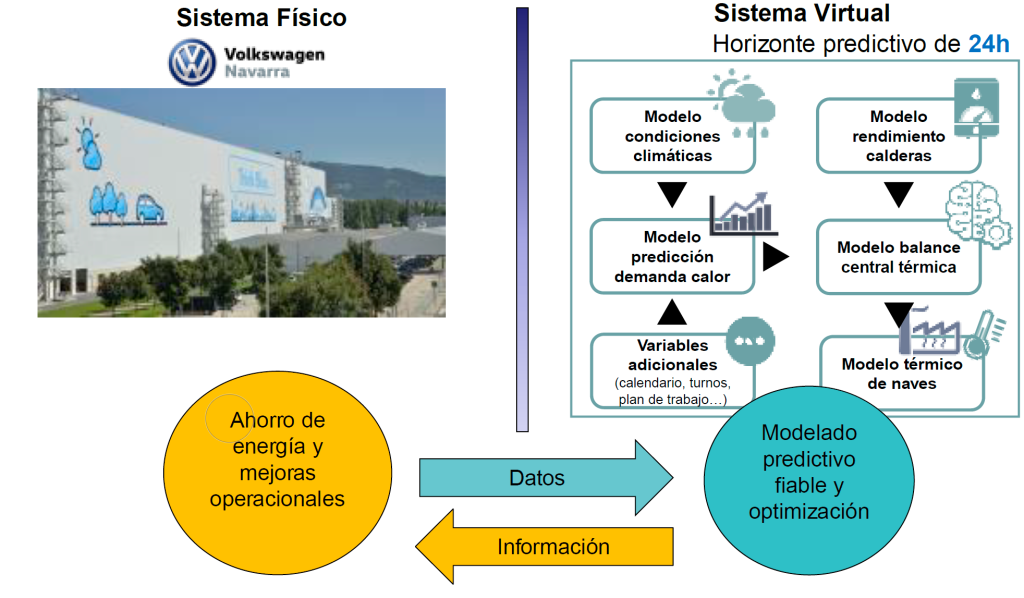
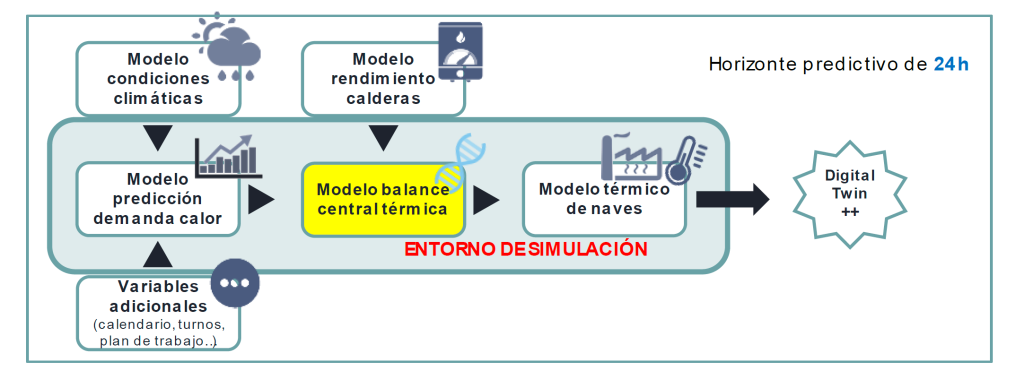
To tackle this problem, AIN-Sistemas Inteligentes proposed creating a digital twin entirely based on data that virtually recreates the industrial climate control system. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system that uses real time data and other sources so learning, reasoning and dynamic recalibration can be done to improve decision-making. A schema of the twin is shown in the attached diagram. One of the greatest difficulties of the project was that the VW NA facilities are extremely complex. To solve that problem, automated and deep learning techniques, genetic algorithms and
other artificial intelligence methods were researched to create more reliable and precise predictive models of the heating needs of the plant and optimise the operations of the thermal power plant in accordance with the predictive model and create a tool that can be used to simulate operating scenarios and study their effect on the temperature of the factory spaces. Integrating each module leads to creating the entirely data based digital twin that makes optimal operating strategies and energy savings possible.
The research process had two phases: 1) complete modelling of all the industrial facilities and 2) building an optimisation and simulation environment that could be used for making operational decisions for the thermal power plant.
The general goal of the project to achieve energy savings was fulfilled. At the beginning of the project it was specified that the reduction would vary depending on external factors (climate conditions, the thermal properties of each building, etc.), but a reduction greater than 5% was pursued. Using data from 2018 as a reference, the savings achieved could be between 3-5% for optimised operation of the thermal plant and 2.5 – 5.8% in start-up / shut down operations.